How Do Photovoltaic Solar Panels Work?
- Insight into the clean energy process
- How solar panels work to convert sunlight into electricity
- Making money from excess electricity
When it comes to solar energy, it’s useful to discover the ins and outs. How solar panels work is relatively straightforward, but there’s plenty to understand throughout the electrical process and beyond. For example, how do solar panels produce carbon dioxide indirectly?
This article will delve into the composition and inner working of photovoltaics. It will explain the electrical process and answer some common queries along the way. The article will then look at how solar panels work to benefit your home and explain how you can use them with low carbon technology.
Interested in photovoltaic (PV) panels already? Use our quote comparison tool to find out how much you’d pay. It only takes a minute.
What's On This Page?
Click the links below and head straight to a specific section of the article.
How Do Solar Panels Work? Composition and Structure
Solar panels are made up of layers of different materials that have an effect on each other. While every panel is made up of smaller solar photovoltaic cells, each cell is composed of semiconducting materials, such as silicon.
Phosphorus is used in the top layer of silicon to add a negative charge. Boron is normally used in the bottom layer to add a positive charge. How solar panels work is through the separation of these conductive materials as it generates an electric field, which allows electrons to be harvested in between the silicon layers.
Metal plates sit on the side of the cells and collect the electrons that are flowing through them. These are then transferred to wires, which is how solar panels generate a usable form of electricity.
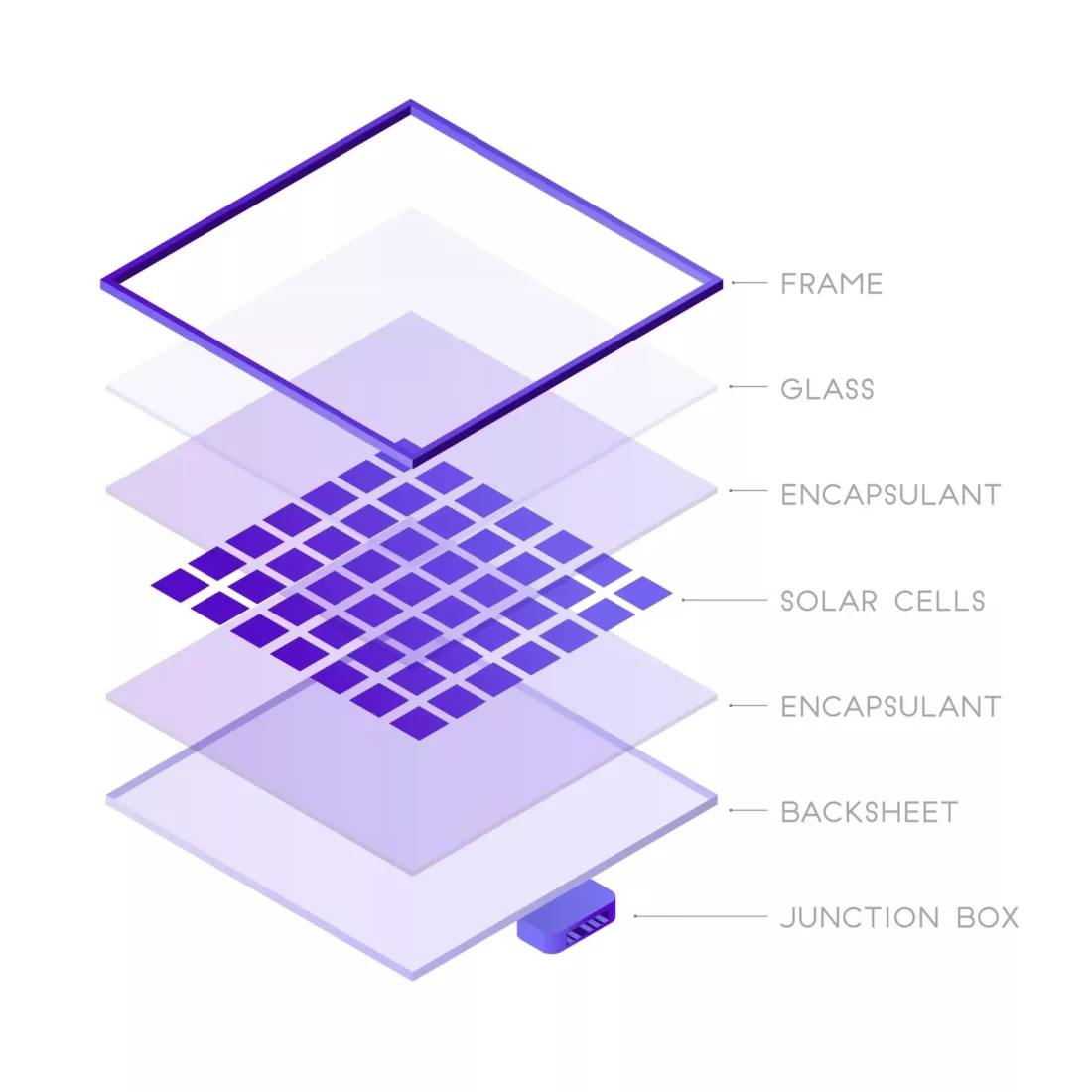
Layers
The solar sandwich is made up of the frame, glass, encapsulant, solar cells, backsheet and then connected to a junction box. These elements serve their own purpose, functioning together to harness energy from sunlight, which is how solar panels work.
Frame
Typically made from aluminium, the frame keeps all of the layers together, preventing movement, bending and cracking. It keeps the panel flat and stable so it lasts. As an added layer of protection, the frame prevents water getting in.
Glass
How do solar panels work without glass? They don’t – or at least they won’t last. The glass helps protect the cells from external damage while also collecting, transmitting and reducing light reflection. This helps maximise electricity generation.
Encapsulant
The encapsulant, or encapsulation film, serves as an insulating and waterproofing element. They help secure the solar cells in place to prevent movement and any corrosion or damage.
Solar Cell
Solar cells are either P-type or N-type. P-types are the most common as they are cheaper. They’re full of positively charged “holes” or areas devoid of electrons, which become the main conduits for the electric current.
How solar panels work with N-type cells is slightly different. N-types have more valence electrons, which make them more efficient at conducting electricity. When it comes to future technology, N-types will most likely take over.
Backsheet
As an additional layer of environmental protection, the backsheet plays a crucial role in how solar panels work. The quality of the backsheet determines the life of the whole module. Once it fails, environmental damage will eventually make the module worthless.
Junction Box
Perhaps the most critical component in the entire make-up of the structure, the junction box is the safe electrical connection between the solar panels and the electrical system it’s connected to. It prevents electric shocks, overheating and allows you to use the energy produced.
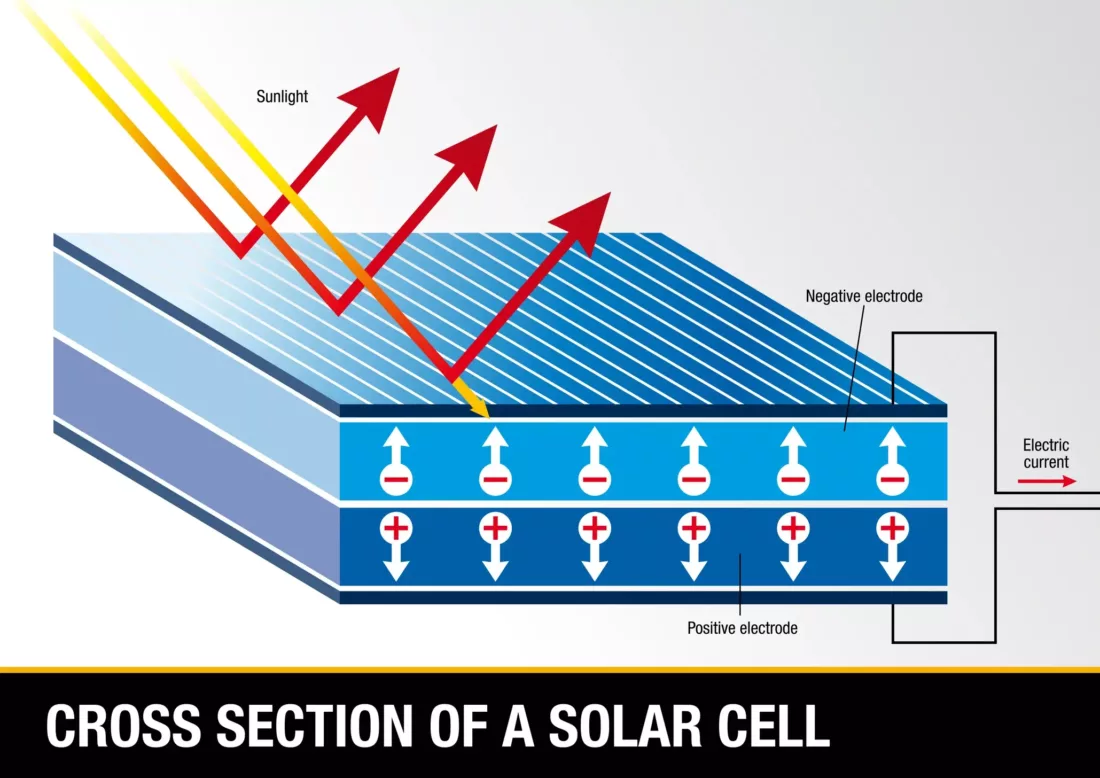
The Photovoltaic Effect
To understand how solar panels work and how electricity is produced, you need to look at the molecular structure. Thanks to the electric field in the panels, caused by the separation of a positive and negative layer, positively charged electrons are able to move through the structure and turn into usable electricity.
How solar panels work to produce electricity is through contact with the Sun. Photons from sunlight smash into the atoms in PV cells, charging the electrons. It’s this charge that is harnessed into a direct current, transferred through the junction box and into your home.
How Do Solar Panels Work? Do They Produce Heat?
Technically, PV panels produce a small amount of heat as they work, but this is released into the atmosphere. How solar panels work to dissipate heat is in their structure. Thanks to its composition, most of the Sun’s energy is reflected back off panels due to a mixture of silicon and glass.
Solar panels are only roughly 16–20% efficient, which means not all energy that reaches them is turned into electricity. While some heat is reflected, constant exposure warms them up. When outside peak operating temperatures, PV panels are less efficient. The hotter they become, the less energy they can generate. They still work on cloudy days though.
Converting Sunlight Into Electricity: How Solar Panels Work
When generating power from PV cells, you cannot simply plug these into electronics as they work on very different voltages. It’s not how solar panels work. They produce varying voltages depending on how much sunlight they receive at any one time. Plugging any device straight into rooftop PV panels may not provide an effective or efficient load and cause fluctuations in voltage and current.
In effect, how solar panels work is by producing a direct current (DC). In order for it to become usable in the home, it needs to be transferred into alternating current (AC). This is what household appliances run off.
While a junction box will provide somewhere for the current to flow from the solar panels, the variable DC electricity needs to be converted to AC. This is where a solar inverter comes in.
How Do Solar Inverters Work in a PV System?
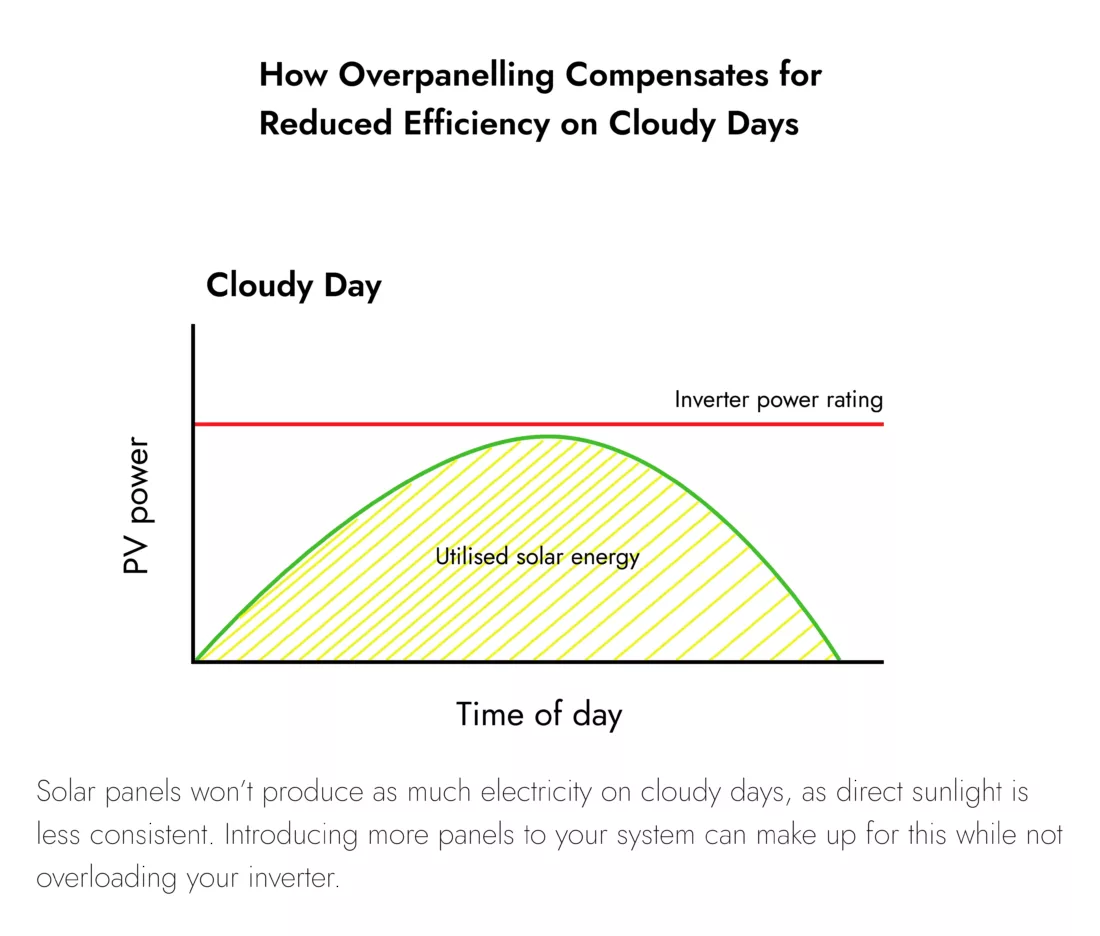
Put simply, an inverter safely converts DC to AC power before feeding it to your home. The inverter runs DC through a transformer to spit it out as AC. However, how solar panels work with an inverter can be problematic. Inverters are limited to a total load. The bigger your solar array, the more electricity they can generate, but there can be too much for the inverter to handle.
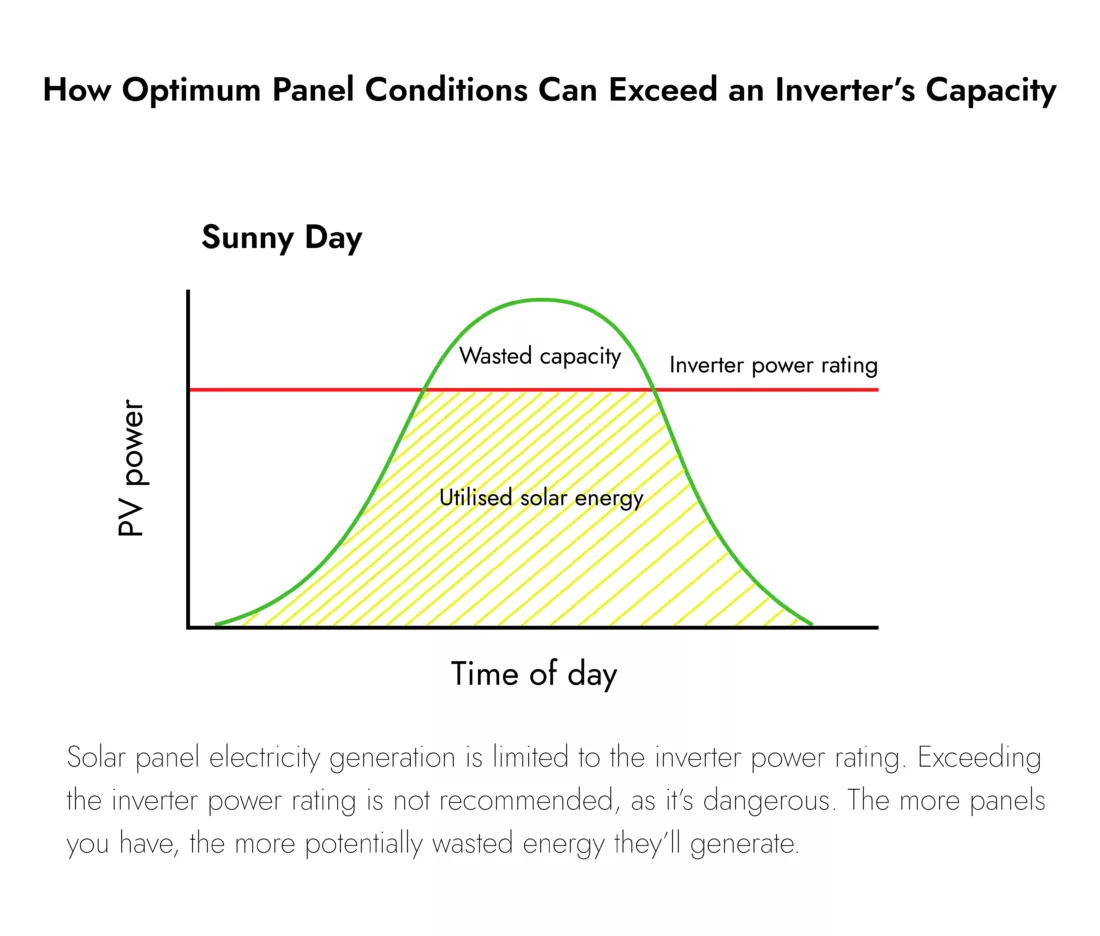
You can get around how solar panels can work with your inverter by installing more. On cloudy days, you can compensate for lost potential whilst not exceeding your inverter’s power rating.
Types of Solar Inverter
How solar panels can work with an accompanying battery is through two types of inverter.
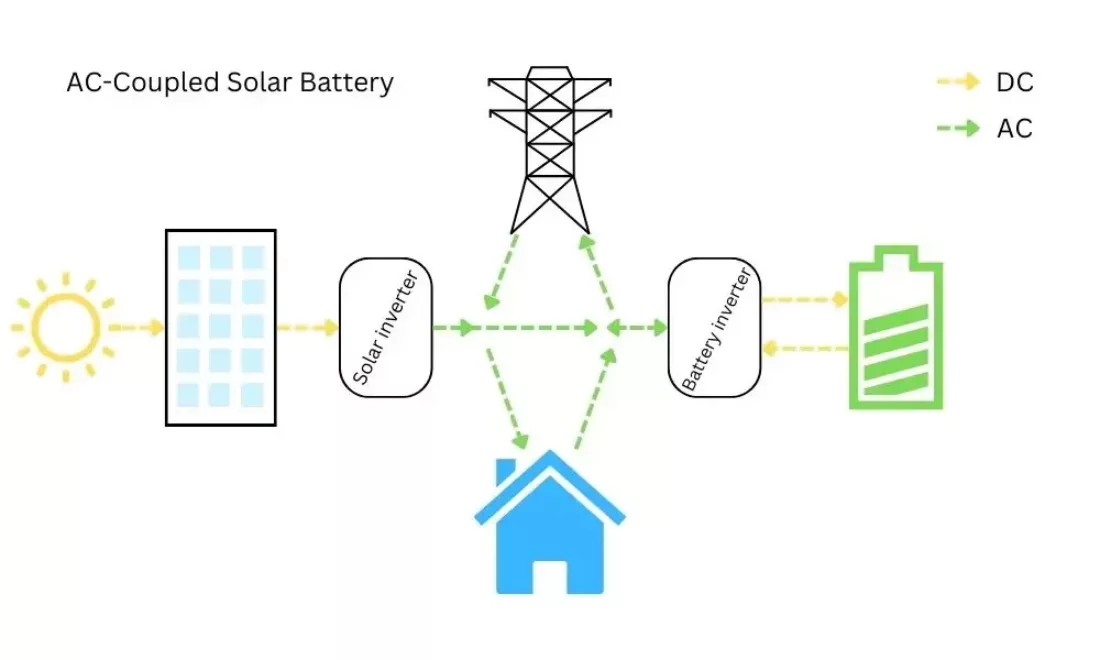
AC-Coupled System
Most homes will have an AC-coupled system with their battery. This means an inverter will convert DC to AC, and if the power isn’t needed, the battery inverter will convert it back from AC to DC in order to store it in the battery. When called for, the battery inverter converts stored DC into usable AC again.
DC-Coupled System
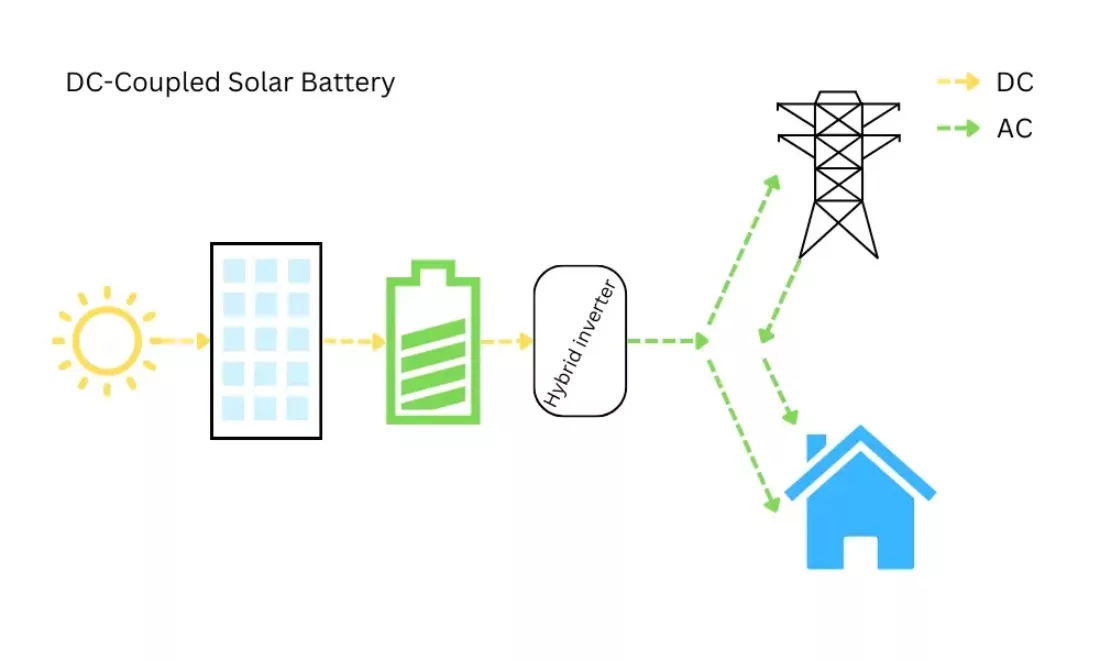
How solar panels work with DC-coupled batteries is simpler. The DC power from the solar panels is stored directly into the battery. A hybrid inverter will then convert it to AC for either use in the home or exporting back to the grid.
Fortunately, hybrid inverters can direct part of the wasted potential above its power rating into an accompanying battery, as it’s still DC electricity.
How Does the Solar Grid Work?
In actuality, it’s incredibly difficult to be off-grid with solar power. In all likelihood, your solar system will be connected to the grid. This then allows you to export any surplus back to the national grid. In a way, any home with PV panels is part of the solar grid, along with solar farms.
By supplementing the grid with solar power, it reduces the stress from transmission over long distances at peak times. Solar energy is usually kept in the area it’s generated, not needing to be sent long distances. Additionally, solar energy smooths out the demand curve, limiting the amount of energy companies need to produce at peak times.
A fully functioning solar grid will make use of energy storage. This gives you power at night when there is no energy source to generate electricity. For homes, this is the difference between using your generated electricity when you’re home or relying on the grid.
How Solar Panels Work With Low Carbon Technology
Having a form of renewable energy in your home is all well and good, but you can go one step further and use it to power low carbon technology. The perfect example of this is how solar panels can work with a heat pump.
Photovoltaics can heat an electric element in a water storage tank. An accompanying air source heat pump will then work more efficiently to provide stored hot water. Alternatively, they can simply power a heat pump directly, limiting how much you import from the grid.
You can see how solar panels work to charge an EV in our accompanying guide.
Environmental Impact
Even though they don’t generate any emissions when they’re producing energy, PVs indirectly contribute to emissions through their lifecycle. Mining, production and transportation all need to be factored in.
The International Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) estimates the total emissions from 1kWh of rooftop solar energy is 41g of CO₂ equivalent. Thanks to how solar panels work, without adding emissions during use, that’s 12 times less than natural gas and 20 times less than coal throughout the whole lifecycle.
Benefits of Solar
You can see how solar panels work for you, but there are a wide range of benefits you can enjoy when you install solar panels.
For starters, you will save money on your electricity bill. By not being susceptible to constant shifts in the energy price cap, you won’t feel the effects of these as much because your electricity imports will drop. This helps reduce your dependence on the grid and your carbon footprint at the same time.
Also, how solar panels work has improved, being designed to last at least 25–30 years, or even longer. This gives you more value for your money over time, especially seeing as you can earn money by exporting excess electricity to the grid.
How Do Solar Panels Feed Electricity Back Into the Grid?
How do solar panels work when there’s no requirement for the energy? When solar energy is being generated but it isn’t being used or stored, a grid-connected system will simply export it to the national energy supply. The power simply runs from PVs to the inverter and then through to the grid. Nothing is ever wasted. And, thanks to government incentives, you can earn money for this as well.
The Smart Export Guarantee (SEG) is the latest programme that pays homeowners for any solar energy they export. Thanks to how solar panels work in this scheme, the licensee you choose doesn’t have to be your existing energy supplier; however, some of the best rates are reserved for their own customers. You’ll usually be paid for every kWh of electricity you export at a rate that legally has to be above £0.
Start Your Solar Journey
Now that you know exactly how solar panels work, why not think about a solar panel installation for your home? The advances in technology have improved efficiencies and lowered prices, so there’s never been a better time to receive these energy savings.
Find out how much solar panels cost in your area by clicking on the button below. You’ll receive tailored quotes from local suppliers.
Related articles
View all Solar Panel articles
Can You Get a Grant for Solar Panels in Scotland?

A Complete Guide to Caravan Solar Panels

Are Solar Panels Worth It in Wales?

Project Solar UK: Company Overview

Battery Storage for Solar Panels Explained

Solar Panel Kits Explained - Everything You Need to Know

Are Solar Roofing Tiles Worth It?







