The Advantages and Disadvantages of Heat Pumps
- Main advantages of heat pumps
- Know the disadvantages before getting a heat pump installed
- Comparison of air source and ground source heat pumps
A heat pump is a low carbon heating technology that moves heat from one place to another using electricity. Their output is much higher than the energy it takes to power them, so they are much more efficient than other alternatives to gas and electric boilers. You can get a heat pump system in two main types: air source and ground source. While other types are available, these are the most commercially available.
This article will delve into the various heat pump advantages/disadvantages and compare them for both air source and ground source types. Broadly, they are similar, but minor differences could help you choose one over the other, depending on your situation.

What's On This Page?
Click the links below and head straight to a specific section of the article.
Heat Pump Advantages/Disadvantages: Overview
Whether you’re looking at air source heat pump advantages or are more concerned about ground source heat pump advantages, heat pumps in general have great benefits. Not only are they a lower carbon alternative for home heating, they can be paired with solar panels as well to help offset any cost. They’re also incredibly energy efficient.
See our related article on heat pump efficiency for more information.
Combining a heat pump with a solar system gives you greater control over your finances and your carbon footprint. While electricity generation in the UK has moved more towards renewable generation, it isn’t necessarily guaranteed from your energy supplier. By utilising your own solar panels to power your heat pump, you can be safe in the knowledge that you’re not contributing to emissions.
Air Source Heat Pump Advantages
Air source heat pumps are advantageous in a number of ways. Mainly, you can enjoy the following benefits:

Lower running costs
High efficiency rating (usually 300%)
Low maintenance
Long lifespan (15 years)
Safe to use (no gas maintenance required)
Reduced carbon emissions
No direct emissions
Provides cooling in the summer
Space and hot water heating
Boiler Upgrade Scheme cost reduction (£7,500 off)
No VAT
To break it down, the air source heat pump advantages almost seem too good to be true. They don’t take as much electricity to run as other heating types as they are highly efficient, typically up to 300%. This means that they can generate 3kW of heat for every kW of electricity supplied to them; they always generate more energy than they use.
The low maintenance required for air source heat pumps is useful when prolonging their life. You can expect a standard air source heat pump to last around 15 years, but easy maintenance will not cause this to be a chore. Compared to a gas boiler, you won’t need to pay for a Gas Safe registered installer to inspect it on a yearly basis, for example. This also makes them much safer because you don’t have to worry about any carbon monoxide leaks.
All heat pumps have reduced emissions because they don’t have any direct emissions from use. They don’t burn fossil fuels and simply use the heat that’s already available in the environment. As well as this, they can essentially work in reverse, providing cool air in the summer instead of heating your home to uncomfortable levels.
In terms of finances, the air source heat pump advantages on offer come in the form of no VAT for the next five years (from April 2022) and the government’s Boiler Upgrade Scheme, which offers £7,500 off the installation of an air source heat pump.
Disadvantages of Air Source Heat Pumps
There are always drawbacks to everything, and a heat pump system is no different. Air source heat pumps come with the following drawbacks:
- High cost
Lower heat supply than boilers
Requires significant work to install
Still use electricity (not necessarily green)
Not fully carbon neutral
Indirect emissions (through electricity)
Not as efficient in cold weather
Needs good insulation from the onset
Do generate some noise
A heat pump does come with a large price tag, compared to other sources of home heating. An air source heat pump can set you back between £12,000 and £17,000. As such, the installation can be tricky. You may need bigger radiators to cope with the lower heat output heat pumps supply, which can push costs up even more.
Read more about air source heat pump costs here.
And while air source heat pumps are a lower carbon alternative, they still use electricity. On top of this, it’s not necessarily produced in a sustainable way. In winter, for example, when temperatures are lower, an air source heat pump needs to use more electricity because it will be operating less efficiently.
On top of these disadvantages of air source heat pumps, one of the biggest issues is that your home needs sufficient insulation in order for the heat pump to work properly. Having installed a heat pump, you’ll need to ensure your home is well insulated beforehand. The high efficiency ratings are only compatible with a home that doesn’t allow heat to escape as quickly. Additionally, air source heat pumps do produce some noise.
Ground Source Heat Pump Advantages
Ground source heat pumps are slightly more efficient than their air source counterparts. Typically, they offer the following benefits:
Lower running costs
High efficiency ratings (usually 400%)
Low maintenance
Long lifespan (20 years)
Safe to use (no gas maintenance required)
Reduced carbon emissions
No direct emissions
Provides cooling in the summer
Space and hot water heating
Virtually silent
Adds value to your property
Boiler Upgrade Scheme cost reduction (£7,500 off)
No VAT
Similar to air source heat pumps, ground source heat pump advantages are almost the same, if not better. The efficiencies of ground source heat pumps are usually around 400%. They generate 4kW of heat for every kW of electricity they use; they generate more power than air source heat pumps.
Ground source heat pumps also have low maintenance. With fewer moving parts than combustion boilers, they are more reliable. The pipes themselves can even last up to 50 years, while the typical lifespan of the heat pump will be around 20 years. Just like air source heat pumps, there’s no gas maintenance needed either.
There’s no direct emissions from ground source heat pumps as they use what heat is available in the ground year-round. This stays at a relatively consistent 8-12°C, which is why they can operate so efficiently. Ground source heat pumps can also provide cooling in the summer, unlike traditional heating systems.
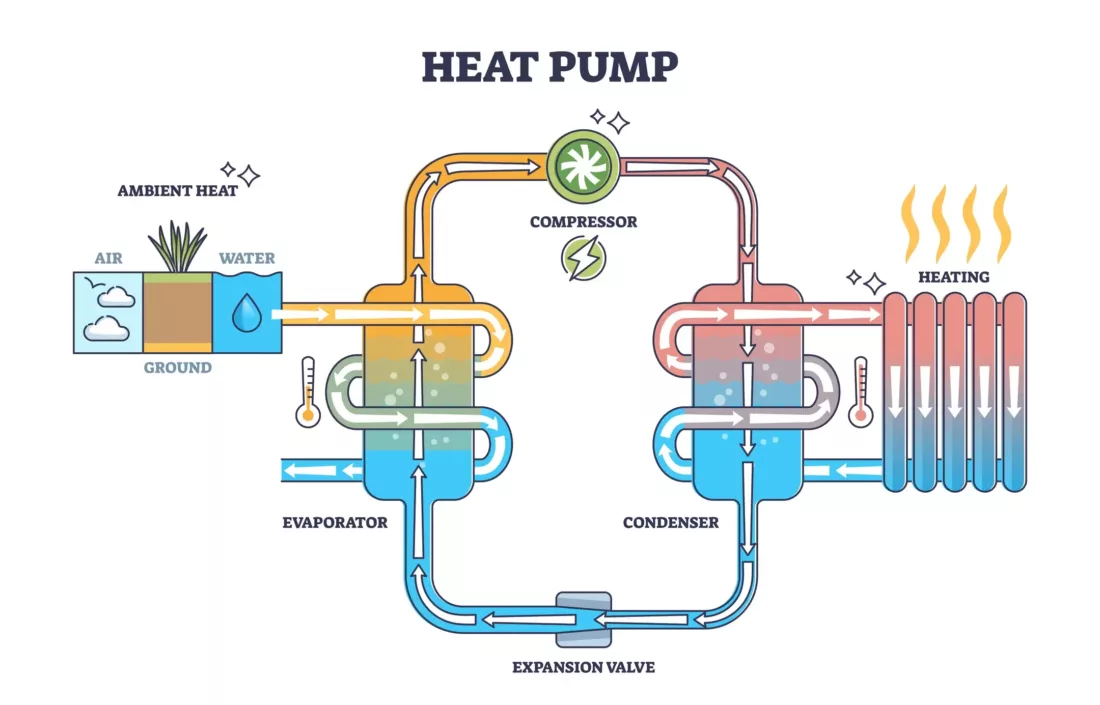
The additional ground source heat pump advantages over air source heat pumps is that they are virtually silent in their operation and they can also add value to your home. New property owners are increasingly looking for homes that feature green systems, and a ground source heat pump, if properly installed and highly efficient, could increase your home’s value. It will offer reduced energy bills as an additional incentive.
With cost in mind, ground source heat pumps also come with no VAT for the next five years (from April 2022) and qualify for the government’s Boiler Upgrade Scheme, which gives you £7,500 off its installation.
Ground Source Heat Pump Disadvantages
Ground source heat pumps and their disadvantages are similar to air source heat pumps, but they work slightly differently. They operate well in cold weather, for example. The main disadvantages are:

High cost
Lower heat supply than boilers
Requires significant work to install
Still use electricity (not necessarily green)
Not fully carbon neutral
Indirect emissions (through electricity)
Soil type affects efficiency
Needs good insulation from the onset
Unlike the cost of air source heat pumps, ground source heat pumps come with a much more premium price tag. Sometimes up to £19,000, this is a significant upfront cost. It’s mainly because of the intrusive installation as the pipes need to be dug into any garden space.
If sufficient room isn’t available, boreholes will need to be drilled into the ground, which doesn’t come cheap. Likewise, you may also need larger radiators to compensate for the lower heat output or install underfloor heating, which is another setback.
Ground source heat pumps are greener, but they still use electricity, which might not be produced using renewable technology. The composition of the soil has an impact on how efficiently the ground source heat pump operates. Sandy soil is not as efficient as clay soil, but your installer should be able to compensate for this. It might be grounds for another cost if you need clay soil added.
As with air source heat pumps, the biggest of the ground source heat pump disadvantages is that your home requires a good level of insulation first. Better efficiencies can only be achieved through high levels of home insulation. If you don’t yet have it, this can set you back even more money.
Heat Pump Advantages/Disadvantages: Final Thoughts
When weighing up all the pros and cons of heat pumps, the biggest issue comes with the price. While this is initially high, costs will come down within the next ten years as the gas boiler ban comes into play and the UK starts to move more quickly towards net zero and low carbon heating.
When air source heat pumps were at their cheapest, they only cost around £9,686. Today, they are more expensive, at £12,555. You can see these in the graph below.
You can read more about this in our related article looking into heat pumps eventually matching the cost of gas boilers.
If you’re able to get past the price tag, the benefits of heat pumps, whether air or ground, are many and various. Among the best advantages is that they can save on your household bills and greatly reduce emissions. Low carbon heating is one of the easiest ways in which you can help reduce the effects of climate change whilst still being energy efficient.
You can read more about this in our related article looking into heat pumps eventually matching the cost of gas boilers.
If you’re able to get past the price tag, the benefits of heat pumps, whether air or ground, are many and various. Among the best advantages is that they can save on your household bills and greatly reduce emissions. Low carbon heating is one of the easiest ways in which you can help reduce the effects of climate change whilst still being energy efficient.
Related articles
View all Heat Pump articles
Samsung Air Source Heat Pumps: Overview and Costs

Mitsubishi Air Source Heat Pumps: Overview and Costs

The Cost of an Air Source Heat Pump Service

Heat Pump vs Gas Boiler - What's Better?

Different types of heat pumps: what’s available?

The Ultimate Guide to Vaillant Heat Pumps

How Do Air Source Heat Pumps Work?







